
Electric motors are the unsung heroes of our modern world, quietly propelling a vast array of devices and systems across numerous industries. As the global focus on energy efficiency and sustainability intensifies, innovative motor technologies have taken center stage. One such technology making waves in this arena is the Switched Reluctance Motor (SRM). In this article, we will delve into the recent developments in SRM technology, with a specific emphasis on efficiency enhancements, advanced control strategies, and the diverse applications that have arisen from these innovations.
I. Introduction
Electric motors serve as the backbone of modern industrial, commercial, and residential systems. They power everything from our everyday household appliances to the electric vehicles that are becoming increasingly common on our roads. As energy efficiency and sustainability have become paramount concerns in today’s world, it is crucial to explore innovative motor technologies that can meet these challenges head-on. The Switched Reluctance Motor, or SRM, has emerged as a compelling solution to these demands. This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the latest advancements in SRM technology, focusing on three core aspects: efficiency, control, and applications.
II. The Historical Evolution of SRMs
To truly appreciate the significance of advancements in SRM technology, we must first look back at the historical context. SRMs have a long and storied history, with their roots tracing back to the early 19th century. However, it was only in the late 20th century that SRMs began to garner significant attention due to the convergence of advanced materials, digital control systems, and computational capabilities. In this section, we will provide a historical overview of SRMs, highlighting key milestones and pioneering innovations that laid the groundwork for the remarkable progress we are witnessing today.
III. The Fundamental Operating Principles of SRMs
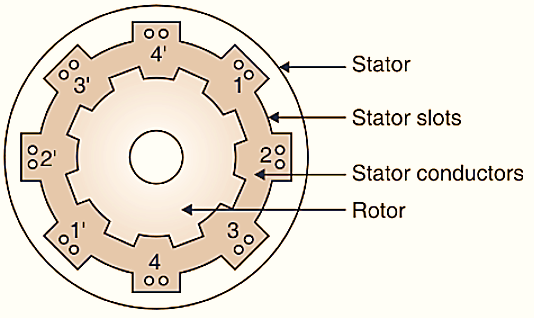
Switched Reluctance Motors operates on principles that distinguish them from traditional electric motors. The core of their functionality is based on the reluctance principle. In this section, we will delve into the basics of SRM design and their unique working principles. We will explore the interaction between the rotor and stator, elucidating the characteristics that set SRMs apart from other motor types and make them particularly suitable for specific applications.
IV. Efficiency Advancements in SRM Technology
One of the key driving forces behind the recent advancements in SRM technology is the quest for improved efficiency. In an era where energy conservation and reduced environmental impact are of paramount importance, SRMs have emerged as an attractive choice. This section delves into the various factors contributing to enhanced efficiency in SRMs, including advancements in materials, magnetic design, electromagnetic modeling, and energy-efficient control algorithms. Through real-world case studies and examples, we will demonstrate how these advancements translate into tangible benefits, making SRMs a compelling option for a wide range of applications.
V. Control Strategies for SRMs
Control is a pivotal aspect of unlocking the full potential of SRMs. The precision and flexibility of control strategies have a profound impact on motor performance. In this section, we will explore the multitude of control strategies employed in SRMs. From sensorless control techniques to advanced digital signal processing and real-time control systems, we will discuss practical applications of these strategies across various industries. Real-world examples will illustrate the effects of these strategies on motor behavior and efficiency, highlighting their adaptability and effectiveness.
VI. Applications of SRMs
The versatility of SRMs has led to their adoption in a wide range of applications, each with its unique requirements and challenges. In this section, we will shed light on the diverse fields where SRMs have made a significant impact. This comprehensive examination will include an in-depth analysis of SRM applications in the automotive industry, industrial automation, renewable energy generation, aerospace, household appliances, and emerging uses in the transportation sector. We will explore the specific advantages of SRMs in these applications and their contributions to enhanced efficiency and sustainability, showcasing their relevance in today’s rapidly evolving industrial landscape.
VII. Challenges and Future Directions
While SRM technology has made significant strides, challenges still exist, and the road ahead promises further innovation. In this section, we will discuss the current obstacles in SRM technology and identify potential areas for improvement. Moreover, we will provide insights into the future trends and innovations expected in SRM research and development. We will examine the role of SRMs in the broader context of sustainable and green technologies, emphasizing the opportunities for growth, integration, and positive impact.
VIII. Conclusion
In conclusion, the recent advancements in Switched Reluctance Motor technology, particularly in the realms of efficiency, control strategies, and diverse applications, are transforming the landscape of electric motors. As industries increasingly prioritize energy efficiency, precise control, and sustainability, SRMs have emerged as a compelling solution. Their potential for a brighter and more sustainable future is undeniable, and they continue to drive innovation and progress across a broad spectrum of applications. As the world seeks cleaner and more efficient motor solutions, SRMs are poised to remain at the forefront of this transformative journey. Their impact on energy efficiency, environmental sustainability, and technological advancement will undoubtedly shape the future of electric motors and the industries they serve.
